Investor Relations
Business Risks

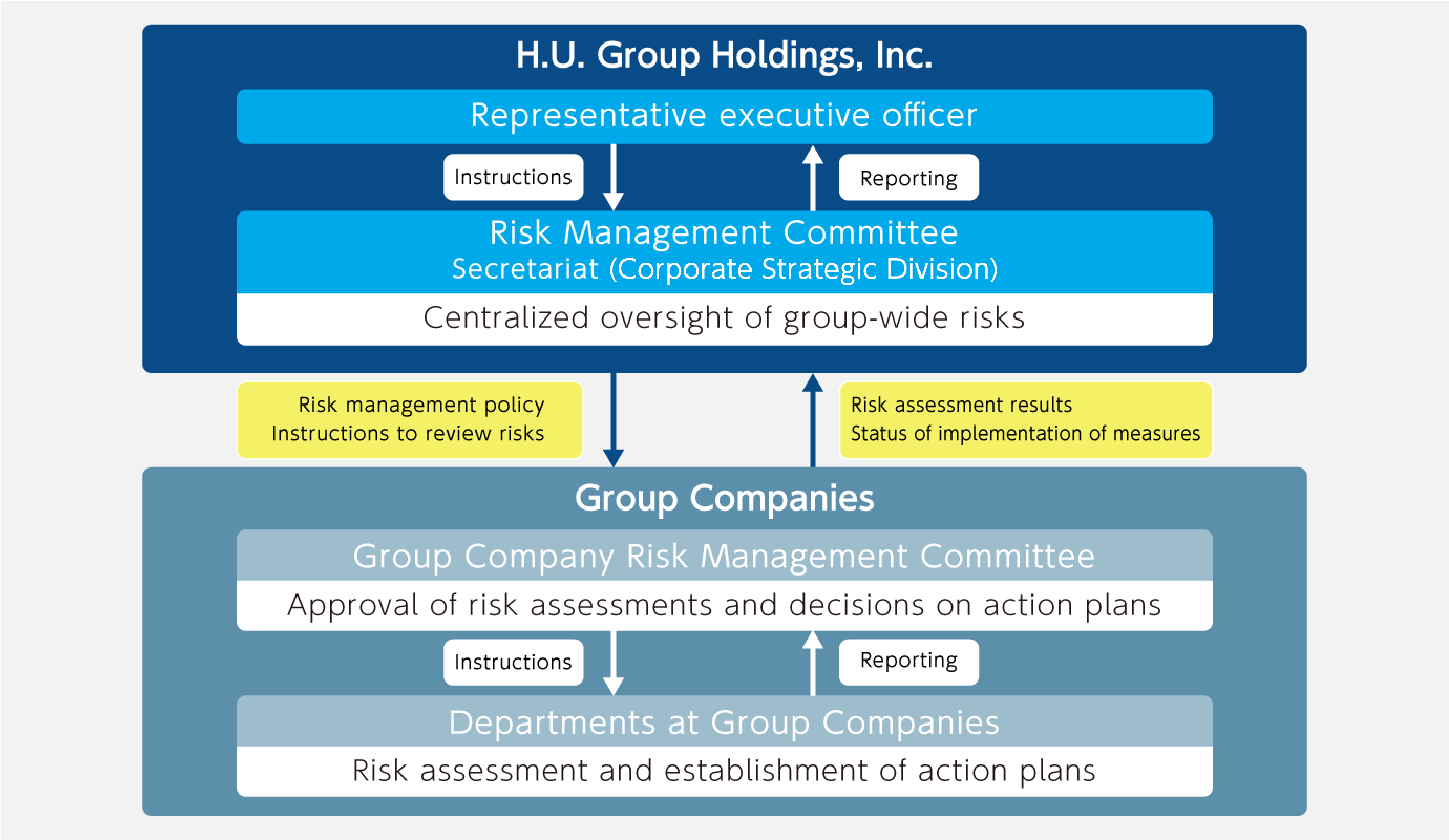
Basic Approach to Risk Management and Management Structure
Risk is managed according to a uniform policy that applies to the entire H.U. Group as defined in the risk management structure within the Risk Management Rules.
The Risk Management Committee was established with the purpose of promoting risk management for the Company and the entire Group. The committee is chaired by the CFO and comprises executive officers other than the representative executive officer. It meets at least annually, with the results reported to the Board of Directors. The committee’s detailed activities include:
- Centralized oversight of the risk management of each Group company;
- Identification of risks facing the entire Group and risks pertaining to the misconduct of management, as well as management of control execution;
- Identification of risks that should be disclosed and management of control execution; and
- Matters concerning the risk management of the Company.
The Company and its Group companies also conduct risk management through the Risk Management Committee or executive committees. This process involves risk identification, categorization of company-wide or business process risks, risk analysis and evaluation based on the possibility and degree of impacts, and risk response. Specifically, risks are managed using a Risk Control Matrix (RCM) and reported at least annually to the Risk Management Committee.
The Risk Management Committee specifies group-wide business risks including significant business risks, taking the status of risk management at each Group company into consideration.
Framework of Group Risk Management
Specific Risks
The Annual Securities Report includes risk factors related to the Group’s business and financial information that may have a significant impact on investors’ decision-making.
Please note that any forward-looking statements contained in this document are based on the Group’s judgment as of the end of March 2025.
Significant Business Risks
(1) Risks related to information handling and information systems
The Group manages large volumes of personal data and patient testing information. Ensuring data security and compliance with Japan’s Personal Information Protection Act is a top management priority. As part of these efforts, SRL, Inc., H.U. Frontier, Inc. and Nihon Stery, Inc., and six other Group companies obtained PrivacyMark certification in February 2005. Additionally, SRL has acquired the Information Security Management System (ISMS) and ISO/IEC 27001 certifications as part of its security measures for operating clinical laboratory testing systems.
The Group operates multiple information systems and strives to maintain stable operations by regularly updating legacy systems and implementing safeguards to prevent data leaks and ensure clear operational protocols being fully communicated and strictly followed.
However, information systems may be disrupted by software or hardware problems, human errors, natural disasters, criminal activities, cyberattacks, viruses, or terrorism. Such events could lead to data breaches, service disruptions, incorrect billing, delayed reporting, or data loss, which could damage the Group’s reputation and adversely impact its business performance and financial condition.
The Group develops of its own information systems to support operations, strengthening project management, including third-party assessments when necessary. However, challenges in securing human resources may delay development, increase costs, or hinder implementation of planned system functions, potentially affecting operational execution and resulting in unrecoverable development costs.
(2) Risks related to quality control and quality assurance
In Lab Testing and its related Services (LTS) business, quality control is essential to ensure testing accuracy. The primary companies involved in LTS regularly participate in quality surveys conducted by organizations, such as the Japan Medical Association, the Japanese Association of Medical Technologists, Japan Registered Clinical Laboratories Association, and other public institutions. These efforts are reinforced by internal quality control and external certifications, including those from the Japan Health Enterprise Foundation, College of American Pathologists (CAP), Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA), and ISO 15189. In the LTS business, the Group swiftly identifies and addresses potential errors through diligent root cause analysis and appropriate countermeasures. Preventative measures include procedural improvements, automation, and enhanced employee training to elevate the standards and minimize errors.
In the In Vitro Diagnostics (IVD) business, the Group enhances product quality through a dedicated internal quality assurance framework. Major IVD group companies hold ISO 13485 certification, the international quality standard for medical devices.
In the sterilization business of the Healthcare-related Services (HS) business, key sterilization centers have obtained ISO9001 certification, the international standard for quality management systems.
Despite these measures, quality-related issues may still arise from human error or unforeseen circumstances, potentially harming the Group’s reputation and adversely affecting its business and financial performance.
(3) Risks related to research and development and technological innovation
The Group actively invests in R&D to drive timely and efficient innovation. H.U. Group Research Institute G.K., serves as a central entity for efficient and speed-up basic research and internal information integration. The Group monitors market trends and participates in academic conferences to gather insights and leverage external expertise. Also, progress is reviewed periodically to ensure effective project oversight internally.
However, the Group may face delays or underperformance due to difficulty in secure human resource. In some cases, projects may be discontinued if they fail to meet regulatory efficacy or safety requirements, leading to unrecoverable costs. Failure to respond to rapid technological changes could also diminish the competitiveness of Group's products, services, or business model, adversely affecting its performance and financial condition.
(4) Risks Related to Human Capital
Guided by the personnel philosophy that “the power of the Company is the sum total of the power of its individual members,” and the Group considers human resources to be its most crucial management asset. It works to secure human resources, develop HR systems, implement career development programs, and create supportive work environment to maximize employee performance.
However, if these initiatives are not effectively implemented, combined with Japan’s declining birthrate and aging population, as well as global labor market shifts, the Group may face difficulties in securing and retaining human resources. Insufficient human resource development could disrupt business operations and adversely affect the Group’s performance and financial condition.
(5) Risks from human-made disasters and infectious diseases
Human-made disasters (e.g., fires, labor disputes, facility accidents) and outbreaks of infectious disease occurred at the Group’s business sites could disrupt operations and adversely affect its business performance and financial condition. In particular, pandemics with high transmission rates and significant health risks may result in operational limitations and additional costs, further affecting performance.
(6) Risks from natural disasters and climate change
The Group has established a robust business continuity plan (BCP) to address potential large-scale natural disasters, such as typhoons and earthquakes. Emergency-use facilities and essential supply stockpiles are maintained at business sites and for medical institution customers.
In alignment with the recommendations of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosure (TCFD), the Group analyzes climate-related risks and chances, integrates findings into strategy, and publicly disclose progress toward achieving carbon neutrality by 2050.
However, if natural disasters or other climate-related damage intensify, they could adversely affect the Group's performance and financial condition. Furthermore, if environmental regulations, such as those governing greenhouse gas emissions, become stricter than expected, the Group’s operation may face additional challenges.
(7) Risks related to the supply of products and services
To maintain a stable supply for its products and services, the Group builds resilient procurement system and diversifies its supplier base.
However, supply chain disruptions caused by unexpected demand increases, delays, malfunctions, or unforeseen external events may impair the Group’s ability to maintain stable delivery. Furthermore, if rising labor or material costs cannot be passed on through pricing adjustments, the Group’s business performance and financial condition may be adversely affected.
(8) Risks related to impairment accounting
The Group holds a diverse portfolio of tangible and intangible fixed assets, including goodwill and investment securities. Among the assets that may have a significant impact on the financial statements for FY2025 are the tangible and intangible assets of SRL, Inc. valued at 51,838 million yen (18.5% of consolidated total assets), investment securities of Baylor Genetics Holdings, Inc. totaling 947 million yen (0.3% of consolidated total assets) and loans receivable of 4,859 million yen (1.7% of consolidated total assets) related to Baylor Miraca Genetics Laboratories, LLC.
These valuations based on accounting estimates. If the value of these declines or their future cash flows falls short of expectations, impairment losses may need to be recognized, which could adversely affect the Group’s business performance and financial condition.
Business Risks
(9) Risks related to M&A
The Group pursues domestic and international M&A to support its growth strategy and enhance corporate value.
Each acquisition is proceeded by thorough due diligence in cooperation with Group companies, relevant internal departments, and, when necessary, external advisors, such as lawyers and accountants.
Despite these efforts, acquired businesses may not perform as expected due to unforeseen post-acquisition circumstances, which could adversely affect the Group’s business performance and financial condition.
(10) Risks related to intellectual property
The Group’s protects its products through patents covering substances, manufacturing methods, and other intellectual property for a certain period. It appropriately manages intellectual property rights, including patent rights, and remains vigilant against infringement by others. To enhance expertise and oversight, it is strengthening management system by consolidating intellectual property management functions within the Group.
However, infringement by or against the Group’s may result in legal disputes or financial losses.
(11) Risks related to statutory regulation
The Group complies with domestic and international regulations, including Japan’s Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Act and the U.S. FDA regulations. It continuously monitors regulatory developments and evaluates appropriate responses.
However, future changes in laws or regulations may restrict operations or increase administrative costs.
(12) Impacts caused by changes in the market environment
Ongoing reforms in Japan’s medical system and intensifying competition present a challenging environment. The Group continuously analyzes market and competitor trends to enhance competitiveness and explore new business opportunities.
However, changes in the market environment, stricter global cost-containment policies or regulatory constraints on R&D, production or trade may adversely affect the Group’s business performance and financial condition.
(13) Risks related to overseas business expansion
The Group actively operates business across North America, Europe, Asia, and other region, making its overseas operations strategically important. However, these activities expose the Group to a variety of risks, including economic downturns, policy changes, economic sanctions, labor issues, cultural differences, political and social instability, weak industrial infrastructure, public hygiene issues, changes in laws and regulations, tax system revisions, terrorism and conflicts, pandemics, and natural disasters. While the Group takes responsive measures to address these risks, they may still disrupt operations and affect its business performance and financial condition.
(14) Risks related to the recoverability of deferred tax assets
The estimation of future taxable income, prior to temporary differences, used to assess the recoverability of deferred tax assets is based on the approved FY2025 budget and the Group’s medium-term management plan, with adjustments reflecting historical performance. This estimate considers the taxable income and losses, excluding temporary factors that occurred in FY2024.
The assessment of deferred tax asset is influenced by progress of FY2025 budget and medium-term plan. If the Group’s performance in FY2025 falls significantly short of expectations, it may become necessary to reduce the recorded amount of deferred tax assets, which could adversely affect the Group’s business performance and financial condition.
(15) Risks associated with the execution of management strategy
The financial targets under the Medium-term Plan are forward-looking statements based on the Group’s management targets. Their achievement is subjected to various internal and external risks, including those noted in items (1) to (14), as well as risks, such as intensified competition, price declines, unmet R&D objectives, shifting customer needs, alliance underperformance, global medical system changes, and risks related to overseas business expansion along with foreign exchange volatility.

