Let’s get it right! Understanding
the COVID-19 testing

Each COVID-19 test has its characteristics.
Here we explain the types and characteristics of the tests, which
help you to understand better.

Types and characteristics of the COVID-19 tests
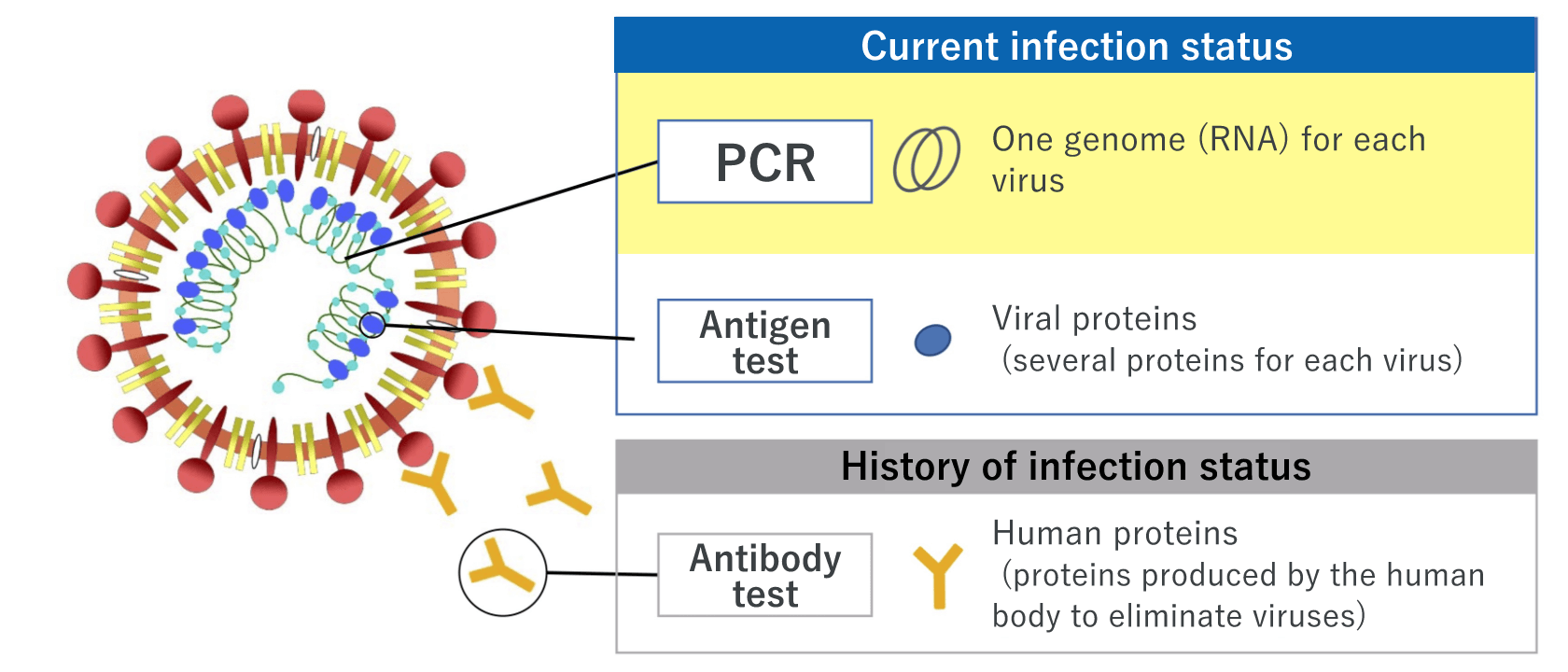
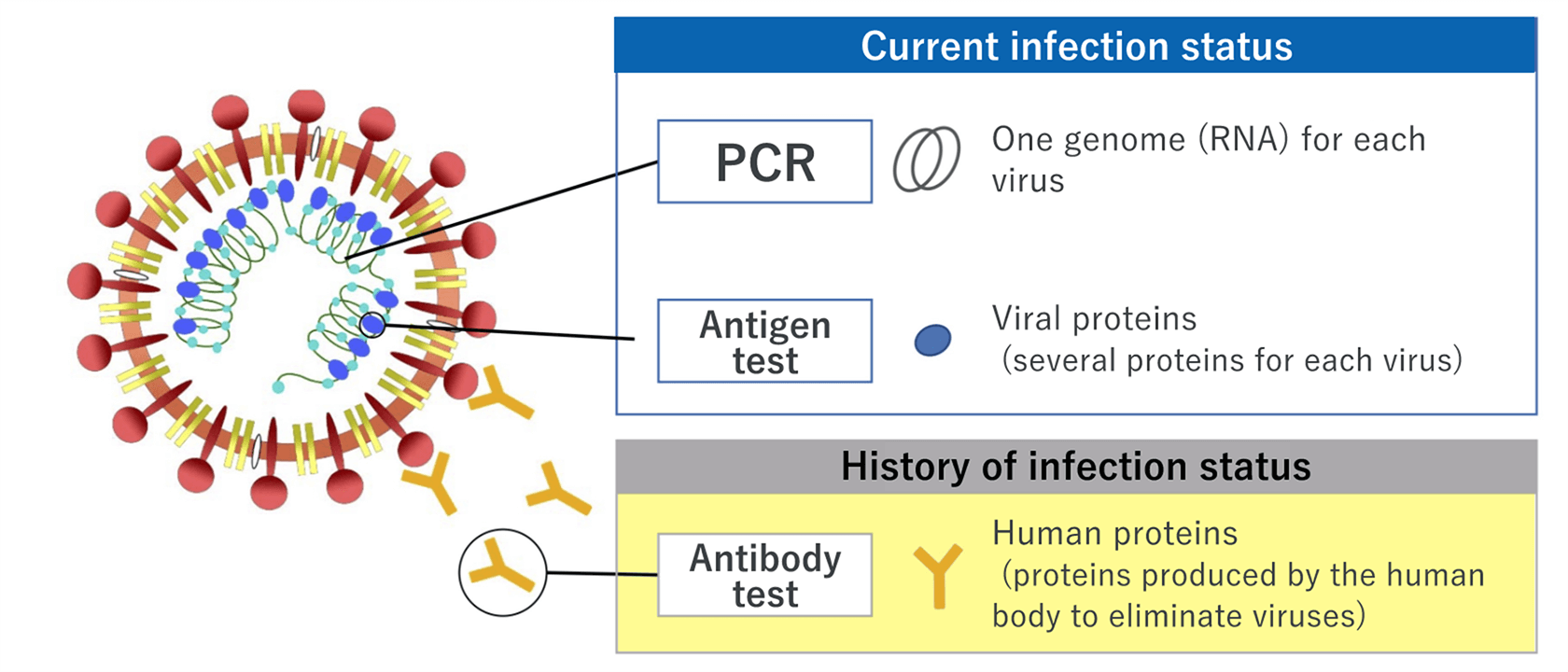
There are mainly three types of COVID-19 tests: Nucleic acid detection tests, antigen tests, and antibody tests.
At medical facilities, tests are usually carried out on clinical specimens in a clinical laboratory center or in-house clinical laboratory. The rapid antigen test, which can be used for point-of-care testing (POCT), does not require any special equipment and can show the results within about 15 to 30 minutes. Currently, this technique is used in Japan and worldwide. Here, we introduce the differences, features, advantages, and disadvantages of each test.
Types and characteristics of tests

PCR - the most popular nucleic acid detection test
The nucleic acid detection test, such as PCR test, involves a method to detect the new coronavirus by measuring the genetic information (RNA) of the virus. The testing sample is saliva or a swab taken from the nose or throat.
■ Features of the PCR test
- can detect even with a small amount of virus
- is widely used from symptomatic to asymptomatic screening
- can be tested at many medical facilities
- performance differs due to various reagents and methods used
- has a risk of contamination (effect of amplified products of other specimens, which result in false positives ) and PCR inhibitory substances ― quality control is important
Antigen test ― gives results within a short time; two types of techniques, high-sensitivity quantitative test and rapid antigen test, are available
The antigen test involves a method to measure viral proteins. There are two types of tests: one is the high-sensitivity quantitative test, and the other is the rapid antigen test. Both are easy and quick to perform. high-sensitivity quantitative test using our products allows using a saliva specimen that can be collected by the patient him/herself, thereby reducing the burden on the healthcare professionals; a saliva specimen cannot be used for the rapid antigen test at this moment.
■ Features of the high-sensitivity quantitative test
- can give a result within ~30 minutes
- has the same level of detection accuracy as some nucleic acid detection test
- can be used from symptomatic to asymptomatic screening
- enables a fully automated system that allows for high-throughput (mass processing) testing using specialized equipment
- can be performed using specialized equipment used in general laboratories
- may require retesting due to non-specific reaction in some cases
■ Features of the rapid antigen test
- can give a result within 15 to 30 minutes
- does not require any special equipment and can give a result at the site
- is effective when a wide range of tests are required, such as in areas where the infection has spread
- could give a false-negative result (a negative result despite being infected) when the viral load is not above a certain level
- is useful for those who are at risk of spreading the infection to others and have sufficient viral load to be detectable
- is not recommended for screening of asymptomatic patients
Antibody test ― shows the history of the new coronavirus infection status
The antibody test involves a method to determine whether the person had the new coronavirus infection in the past and now has antibodies against the virus. An antibody is a protective protein produced by the immune system in response to the elimination of the virus after the infection of the new coronavirus. Antibodies take a while to be produced in the body, so the antibody test is not suitable for determining a person’s current infection status.
■ Features of the antibody test
- can determine whether the person had the new coronavirus infection in the past by using blood samples (1 to 3 weeks after infection)
- cannot determine the current infection status
- does not prove the history of infection status in the past even the negative results
- could give positive results several weeks after vaccination
- may not show the increase in antibody titer after vaccination, which does not mean that vaccine was ineffective
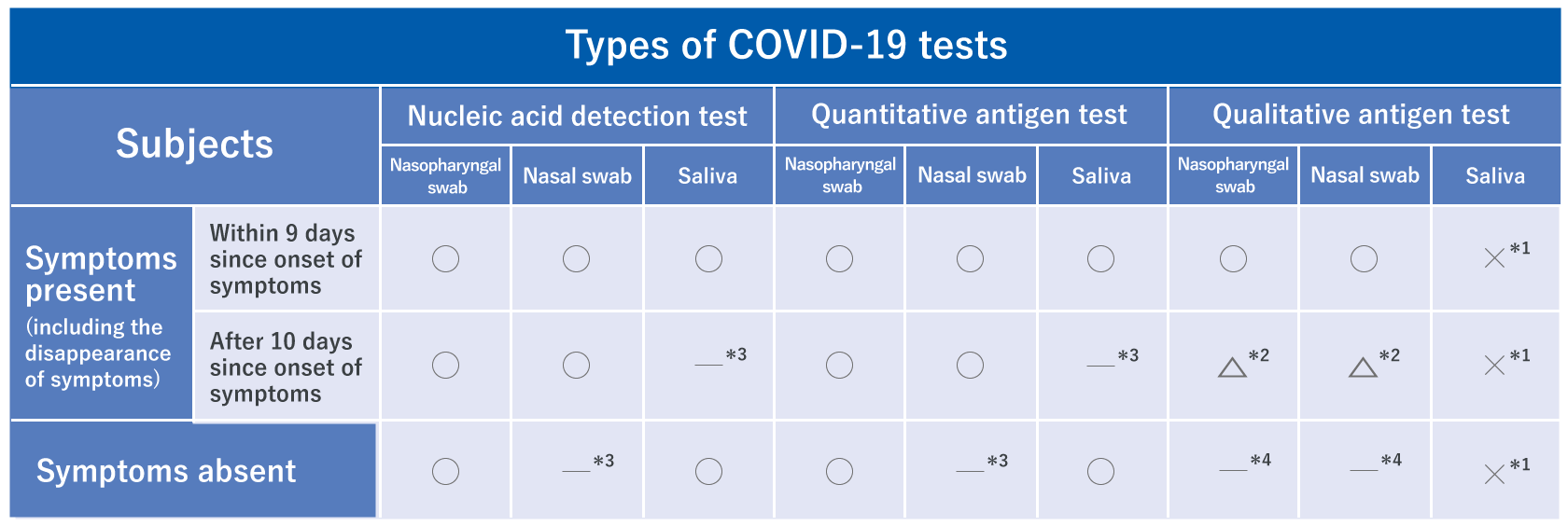
Types of tests and their suitable usage
Since different tests have different characteristics, the test to be performed depends on the situation. It is important to perform the tests in accordance to the situation at hand.
■ Examples of types of tests under different scenarios
- A person who claimed symptoms such as fever, visited a medical facility, and was suspected to have COVID-19.
Nucleic acid detection test
Quantitative antigen test
Qualitative antigen test (within 9 days since onset of symptoms)

- To check the infection status of persons in close contact (including asymptomatic persons) with patients known to have COVID-19.
- Cluster occurred in a medical facility, and there is a need for screening.
Nucleic acid detection test
Quantitative antigen test
Qualitative antigen test

- To perform rapid testing of symptomatic patients in high-risk facilities.

Qualitative antigen test

- To perform rapid and highly sensitive test to check for COVID-19 in a limited environment for a limited number of staff members.

Quantitative antigen test

- Need proof of negative results before overseas business trip.

Nucleic acid detection test
Quantitative antigen test / Qualitative antigen test
(depending on the country)

- To determine the infection status in the past.
- To determine if antibody titer is elevated due to vaccination.
Antibody test

Our efforts for the fight against COVID-19
(1) Pursuit of inspection accuracy
We utilize the experience of our group, which has been involved in clinical testing for over 50 years, to conduct tests based on high-quality standards when we are commissioned by medical institutions. Furthermore, we believe that it is important to provide
stable tests. We have conducted a rigorous evaluation for the new coronavirus test reagents; and we perform tests using selected reagents that have proven efficiency in performance and within the supply system. We also monitor
the test results to ensure the accuracy of the daily tests.
We were the first in the world to develop qualitative and quantitative antigen test reagents, and have been providing them to the
medical field in a stable manner. Third-party studies proved our reagents to be compatible with other companies’ products and show top level detection sensitivity among competitors.

(2) Enhancement of domestic testing
Our group company was the first private testing company to provide contract testing for COVID-19. Since then, we have been providing almost all types of tests, including nucleic acid detection tests such as PCR tests, antigen tests, and antibody tests,
on a 365-day basis throughout Japan. For PCR tests and high-sensitivity quantitative antigen tests, we have a capacity of more than 30,000 tests per day nationwide.
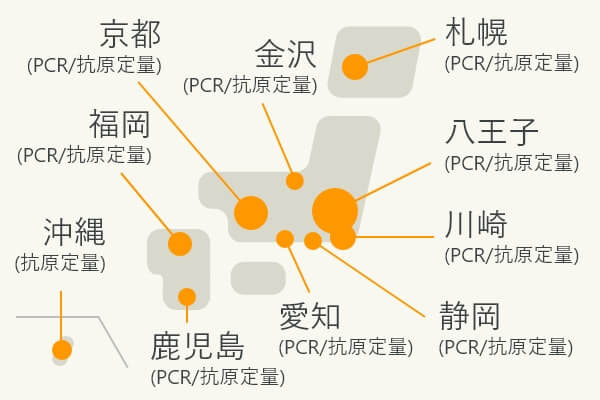 Nationwide test centers
Nationwide test centers (Establishing a nationwide testing system centered on the Hachioji Laboratory)
Our high-sensitivity quantitative antigen testing reagents are available in automated systems to meet various needs. Our products are widely used at university hospitals, testing centers, and airport quarantines. Currently, more than 50 high-sensitivity quantitative antigen testing systems are in operation at eight airports in Japan.
 Inspection scene at the airport quarantine station
Inspection scene at the airport quarantine station
(3) Countermeasures for mutation and further research
■ For reliability
Since viruses mutate easily, the new coronavirus was expected to mutate. Even before the emergence of variants that affect viral replication and immunity as we know today, mutations that might affect test results had been reported. Thus, we carry out analyses and monitoring to check routinely whether the mutations that occur affect the test results and usage of our reagents.
■ Responding to the actual crisis
Since around December 2020, several mutations that might change the characteristics of the new coronavirus have been reported. We have introduced PCR / sequence analysis technology to identify variants, and have contributed to understanding how widely variants are spread.

■ Preparing for a future crisis
Since new variants are expected to continue to occur in the future, we believe that it is extremely important to monitor mutations which might affect the testing and improve testing techniques which detect the variant correctly. We will continue our own research and will check and improve the PCR and antigen tests provided by the H.U.Group on a daily basis to detect any new variants.
(4) Social Contribution
We, at H.U Group donated "ESPLINE SARS-CoV-2" the rapid antigen test kit for new coronaviruses to Nepal in September 2020 and to Pakistan in May 2021. In July 2021, we also donated the kit to the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology
(MEXT) for use in universities and other educational institutions to prevent the spread of infection.
The H.U. Group is working together to prevent the spread of new coronavirus infection.
Q&A for COVID-19 tests
A
Nucleic acid detection test, including PCR test, is a highly sensitive testing method. However, reports have shown varying results using different reagents. The reliability of the results can also vary from facility to facility.
Caution is needed when using this test as it can detect non-infectious viruses in your body even after you recover from infection.
There are two types of antigen tests: the high-sensitivity quantitative antigen test and
rapid antigen test. The high-sensitivity quantitative antigen test has the same accuracy as the PCR test except in cases of low levels of virus in your body when infectivity is often low. The results can be obtained within
as little as 30 minutes. In addition, the use of a fully automated system allows for the simultaneous processing of multiple tests. Thus, it is used at airport quarantine, where results of a large number of tests are required
within a short period of time and at medical facilities that test a large number of patients.
Rapid antigen test is a method that often does not require special techniques or equipment and can provide results on-site in
15-30 minutes. It is useful in clinics with a limited number of clinical laboratory specialists, in time-sensitive emergency medical situations, in medical facilities in areas where the infection is spreading, and in elderly
care facilities for testing individuals with no symptoms.
In both tests, a false negative result (a negative result when the test is actually positive) might occur at the early stages of infection because there are insufficient levels of the virus in your body. Therefore, when
in doubt, you should be tested frequently. The antigen test is suitable for frequent testing because it is easy to use and can help reduce the chance of not detecting the virus at the early stages of infection.
Since each
test has different characteristics, medical professionals will select the most appropriate test based on your situation.
A
You may be infected even if your test is negative, depending on your stage of infection or test sample collection method. In particular, the saliva sample can be affected by smoking, eating, drinking, and mouthwash, so it is necessary to avoid smoking, eating or drinking anything, and brushing your teeth for not spike proteins that are important in viral infections currently causing issues with occurrence of variants, at least 30 minutes before taking a saliva sample. In addition, samples may also contain contaminants that can reduce the ability to detect the virus by PCR tests.
A
The H.U. Group offers PCR and antigen tests (high-sensitivity quantitative antigen test and rapid antigen test), and antibody test.
Reports have shown varying performances of PCR tests depending on the test reagents used. We
select and use reagents that have provided reliable results with actual test samples. In addition, we thoroughly monitor the accuracy of daily testing. Third-party research groups have reported high reliability of our rapid
antigen test. Its detection rate is also the highest among similar testing methods currently available on the market. Our high-sensitivity quantitative antigen test further enhances the reliability of the rapid antigen test.
In clinical studies, it has been shown to have the same level of reliability as the PCR test. In addition, it is the only approved in vitro antigen test that can test saliva samples at medical facilities.
A
PCR test detects genes that are not susceptible to mutation and can detect new variants that are currently causing problems. We also check routinely for changes in the virus that may affect the PCR test. The antigen test detects nucleocapsid proteins, not spike proteins that are important in viral infections currently causing issues with occurrence of variants, and we use multiple antibodies that bind to different positions. In addition, we have confirmed that the test can detect nucleocapsid protein of variants that are spreading and causing problems. In addition to the ingenious design of our method, we monitor the trends of mutations on a daily basis and perform verification and confirmation tests when new mutations are reported.
Types of tests
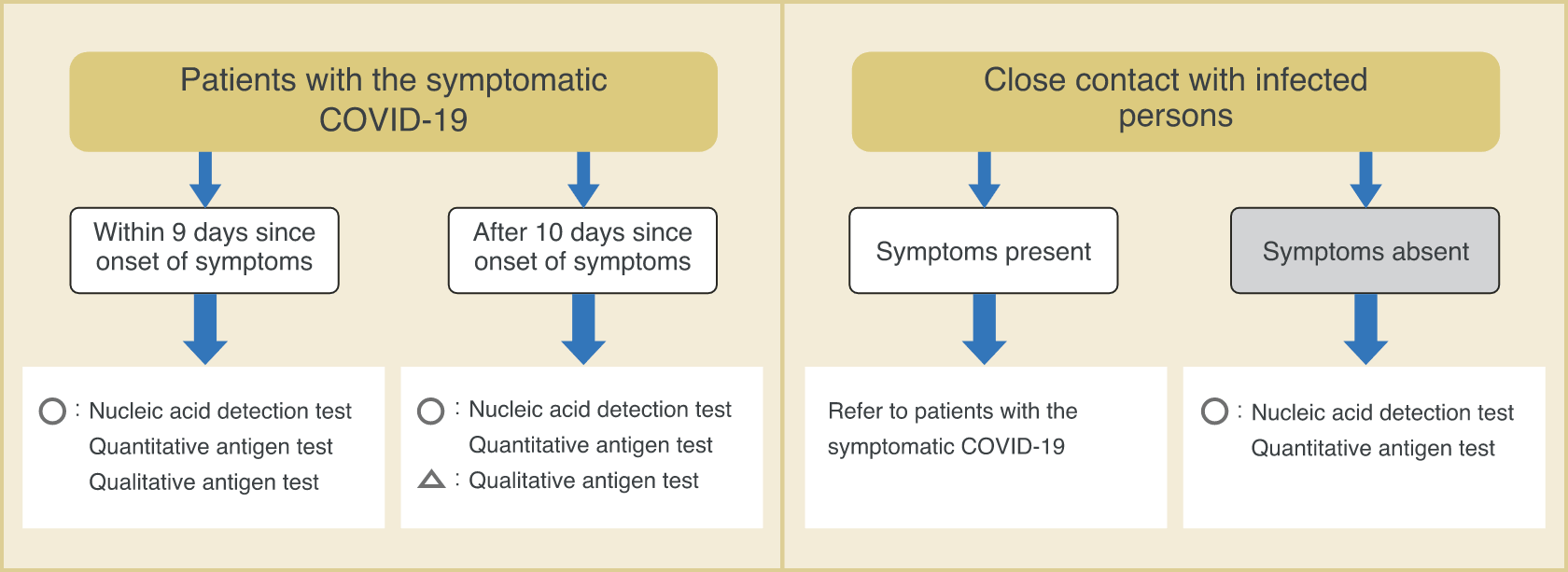
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, et al. New Coronavirus Infectious Disease (COVID-19) Pathogen Testing Guideline Version 4
Targets
Targets
Targets
Appropriate specimen
Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, et al. New Coronavirus Infectious Disease (COVID-19) Pathogen Testing Guideline Version 4

